If you're a plant lover looking to expand your indoor jungle without breaking the bank, propagating houseplants is a fantastic and cost-effective way. It allows you to multiply your plant collection, and it can also be a rewarding experience to witness new life sprout from cuttings. In this article, we will explore the process of growing houseplants from cuttings, discuss water propagation, identify the easiest indoor plants to propagate and determine the best methods for successful houseplant propagation.
Growing houseplants from cuttings is a popular method plant enthusiasts use to create new plants. Here's a step-by-step guide:
Step 1: Choose a healthy parent plant: Select a mature, healthy houseplant from which you want to take cuttings.
Step 2: Prepare the cutting: Using clean, sharp scissors or pruning shears, take a cutting just below a node (the point where a leaf is attached to the stem). Ideally, the cutting should be 4-6 inches long and have at least two sets of leaves.
Step 3: Remove lower leaves: Trim off the lower leaves from the cutting, leaving only the topmost leaves intact.
Step 4: Rooting hormone (optional): If desired, dip the cut end of the stem into a rooting hormone powder or gel to encourage root growth.
Step 5: Plant the cutting: Insert the cut end of the stem into a well-draining potting mix or rooting medium, ensuring it is stable and upright. Keep the soil moist but not waterlogged.
Step 6: Provide proper conditions: Place the cutting in a warm, well-lit location away from direct sunlight. Maintain a consistently humid environment by covering the cutting with a plastic bag or using a propagator. Mist the leaves occasionally to boost humidity.
Step 7: Monitor and wait: Over time, the cutting will develop roots and establish itself as a new plant. Be patient and avoid disturbing the cutting until it has rooted sufficiently.
Can all houseplants be propagated in water? While water propagation is a popular method for many houseplants, not all species can be propagated successfully in water alone. Some plants are better suited for other propagation methods, such as stem cuttings in soil or specialized techniques like air layering. However, numerous common houseplants, including Pothos, Philodendron, Spider Plant, and Chinese Evergreen, can be propagated in water.
When propagating in water, follow similar steps as mentioned earlier, but instead of planting the cutting in soil, place it in a container filled with water. Ensure that only the cut end of the stem is submerged while the leaves remain above the water level. Change the water regularly to prevent stagnation and monitor root development. Once the roots are well established, you can transfer the cutting to a pot with soil for further growth.
What are the easiest indoor plants to propagate? While the ease of propagation can vary among plant species, some houseplants are known to be exceptionally forgiving and suitable for beginners. Here are a few examples:
- Pothos (Epipremnum aureum): Pothos is a popular trailing houseplant known for its vibrant foliage and ability to thrive in various lighting conditions. It is straightforward to propagate, making it an excellent choice for beginners. Take stem cuttings with a few nodes and place them in water or soil. Within a few weeks, you'll start to see new roots forming, and you can then transfer the cuttings to a pot with soil.
- Spider Plant (Chlorophytum comosum): Spider plants are beloved for their arching, variegated leaves, and ability to produce "siderites" or baby plants. These baby plants can be easily propagated by cutting off the spinnerette with a short stem, planting it directly in the soil, or placing it in water. In addition, spider plants are resilient and will quickly establish roots, resulting in a new plant.
- Snake Plant (Sansevieria): Snake plants are known for their striking upright leaves and ability to tolerate various growing conditions. To propagate snake plants, divide the plant by separating the offsets, or "pups," from the main plant. Allow the pups to dry for a few days before potting them in well-draining soil. Snake plants are known for their robust nature, making propagation relatively easy.
- Jade Plant (Crassula ovata): Jade plants are succulents with thick, fleshy leaves that store water. They are known for their resilience and adaptability, making them suitable for propagation. Take stem cuttings from a healthy jade plant, let them dry for a few days to form a callus, and then place them in well-draining soil. Jade plants are slow-growing, but with patience, the cuttings will develop roots and grow into new plants.
- ZZ Plant (Zamioculcas zamiifolia): The ZZ plant is a low-maintenance houseplant with glossy, dark green leaves. Propagation of ZZ plants can be done by dividing the rhizomes or taking leaf cuttings. When dividing the rhizomes, ensure each division has a portion of the rhizome and a few leaves. Plant the divisions in separate pots with well-draining soil. Alternatively, place leaf cuttings in water or soil until new roots and shoots emerge.
The best way to propagate houseplants largely depends on the specific plant species and personal preference. For example, while water propagation is suitable for many plants and allows you to observe root development, other plants may prefer soil propagation or alternative methods like division or air layering.
Therefore, it's essential to research the specific propagation requirements of each plant species to choose the method that yields the best results.
In conclusion, propagating houseplants is a rewarding and cost-effective way to expand your indoor garden. You can quickly grow new plants from existing plants by following simple steps, such as taking stem cuttings and providing the right conditions. Remember to choose suitable plants for propagation, such as pothos, spider, snakes, jade, and ZZ plants, as they are known to be forgiving and beginner-friendly. Experiment with different propagation methods to find what works best for each plant. Happy propagating!
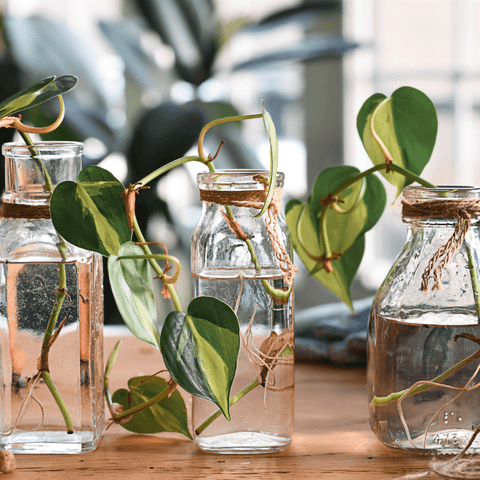



Comments (0)
There are no comments for this article. Be the first one to leave a message!